In Principle:
Genetic Engineering involves the laboratory manipulation of DNA
What does a particular region of DNA do?
This may involve isolation & manipulation of a "gene of interest"
in vivo or in vitro "cloning" of the gene [Nobel Prize 1980]
analysis of the cloned gene
gel electrophoresis
DNA sequencing
mRNA expression
Genetic Engineering involves the laboratory manipulation of DNA
What does a particular region of DNA do?
This may involve isolation & manipulation of a "gene of interest"
in vivo or in vitro "cloning" of the gene [Nobel Prize 1980]
analysis of the cloned gene
gel electrophoresis
DNA sequencing
mRNA expression
DNA sequencing [Nobel Prize 1980]
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) [Nobel Prize 1993]
fresh viral, prokaryotic, or eukaryotic (plant & animal, etc.) material
DNA separated from other molecules by selective binding to beads
(CSHL animation of DNA extraction)
Ancient DNA
museum specimens: 10s ~ 100s years
fossils: 1,000s ~ 1,000,000s years
Ex.: insects in amber
Ex.: ancient humans: Neanderthals & relatives
Forensic DNA
Forensics: data used as evidence
Ex.: blood / semen stains at crime scenes
Ex.: What species do these fillets come from?
In vivo Molecular Cloning of DNA
Type-II restriction endonucleases
cut DNA only at specific restriction sites (list)
DNA palindrome -
"Able was I ere I saw Elba"
"Madam, I'm Adam"
"Straw? No! Too stupid a fad, I put soot on warts."
"A man, a plan, a canal: Panama!"
''Doc, note I dissent. A fast never prevents a fatness. I diet on cod."
"Saippuakivikauppias" - Finnish word for a soap seller
restriction site reads the same in 5'

Overhanging TTAA-5' are "sticky ends"
Vector insertion
Vector - a means of moving DNA from one place to another
Plasmids - a circular, extrachromosomal DNA
"naked DNA", a "bacterial virus"
pUC18 - an artificial plasmid with:
selectable markers that tell you when plasmid is present
antibiotic resistant (e.g., tetracycline or ampicillin)
lacZ gene produces beta-galactosidase,
metabolizes Xgal sugar
lacZ gene includes polylinker
multiple, unique restriction sites
Recombinant DNA molecules are formed when
linearization of vector DNA by digestion with endonuclease
ligation of "sticky ends" between source DNA & vector DNA
combines DNA from two different sources
[online animation]
In vivo cloning in E. coli [IG1 02.18]
E. coli K12 strain
can't grow in presence of antibiotics (antibiotic-sensitive)
can't metabolize X-galactose (Xgal) sugars
Host transformation integrates plasmid DNA into bacterial chromosome
Bacteria acquires genetic traits of plasmid
Colony Selection Scheme: finding the rare bacterium with recombinant DNA
Only E. coli cells with resistant plasmids grow on antibiotic medium;
only plasmids with functional lacZ gene can metabolize Xgal
lacZ(+)
lacZ functional
lacZ(-)
polylinker disrupted
Bulk bacterial culture of recombinant (white) colonies
Purify cloned plasmid DNA, cut cloned gene out with endonucleases:
Gene is ready for Analysis
SUMMARY OF pUC CLONING
Polymerase
Chain Reaction
In vitro DNA "cloning":
"DNA xeroxing": four components & a gadget
DNA template
anything with DNA in it
oligonucleotide primers ("oligos")
short (20 ~ 30 base) ssDNA complementary to gene
some knowledge of gene is required :
"Universal primers" work across many species
Taq DNA polymerase
heat-stable enzyme from hot-spring bacteria (Thermus aquaticus)
functional at 70 ~ 80oC, withstands exposure to 95oC
dNTPs: four building-blocks for DNA
Thermal cycler: computer-controlled heating & cooling block
temperature change > 1oC / sec
PCR doubles gene copy number each cycle
denature / anneal / extend: 2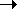 4
4 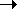 8
8 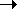 16
16 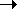 32
32 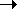 64 etc.:
64 etc.:
10 cycles = 210 = 103 copies, 20 cycles 106 copies, 30 cycles
106 copies, 30 cycles
 109 copies
109 copies
[ of PCR]
PCR process is completely automated
replicates specific gene only
makes sufficient quantities of purified genes for direct analysis
In vitro DNA "cloning":
"DNA xeroxing": four components & a gadget
DNA template
anything with DNA in it
oligonucleotide primers ("oligos")
short (20 ~ 30 base) ssDNA complementary to gene
some knowledge of gene is required :
"Universal primers" work across many species
Taq DNA polymerase
heat-stable enzyme from hot-spring bacteria (Thermus aquaticus)
functional at 70 ~ 80oC, withstands exposure to 95oC
dNTPs: four building-blocks for DNA
Thermal cycler: computer-controlled heating & cooling block
temperature change > 1oC / sec
PCR doubles gene copy number each cycle
denature / anneal / extend: 2
10 cycles = 210 = 103 copies, 20 cycles
[ of PCR]
PCR process is completely automated
replicates specific gene only
makes sufficient quantities of purified genes for direct analysis
Restriction mapping
Determining the order of & distances among restriction sites in DNA fragment:
provides an "outline" of the DNA sequence [IG1 21.22]
(much) finer scale than three-point test cross map
Gel electrophoresis separates DNA fragments by molecular weight
( of agarose gel electrophoresis)
Fragment numbers & sizes compared in single & pairwise restriction digestions:
order & distances among sites determined as Restriction map
(CSHL animation)
Restriction maps of overlapping fragments assembled as contig map
DNA sequencing
in vitro DNA replication copies one strand repeatedly
(cf PCR: both strands replicated)
Provides complete order of bases in a DNA fragment
DNA primer is complementary to 3' end of gene of interest
dideoxynucleotide terminators (ddNTPs)
stop strand growth during replication
four separate reactions terminate at ddA, ddC, ddG, or ddT [IG1 02.19]
Sequencing gel shows series of partial DNA replications
Sequencing "ladder" autoradiogram read from bottom to top
( of dideoxy DNA sequencing)
Automated DNA sequencers uses laser fluorometry
ddNTPs attached to fluorescent dyes in a single reaction
scanning laser activates & fluorometer "see" fluorescence colours (A C G T) [HOMEWORK]
computer "calls sequence" as a chromatogram [IG1 02.21]
( of automated DNA sequencing)
Next Generation sequencing uses massively-parallel, high-throughput methods [IG1 ResBrief 21.1, pp. 454-455]
NextGen sequencers use capillary separation [IG1 02.20]
Southern Blot analysis
Useful when gene of interest rare: one locus / genome
DNA transferred ("blotted") to filter paper
Filter exposed to a DNA probe
Probe: instrument or method that measures something (e.g., thermometer)
ssDNA complementary to gene region of interest
~ same as primer / oligo in PCR experiment
Binds specifically to target DNA immobilized on filter
Radioactive label with 32P-dNTPs
Autoradiogram shows presence / absence & size of target DNA
RFLP differences
Click here to go to the download site