In principle:
We can extend single-locus ![]() multilocus
multilocus ![]() quantitative models
quantitative models
1AA
: 2Aa : 1 aa ![]() (1AnAn : 2Anan : 1anan)n
(1AnAn : 2Anan : 1anan)n ![]() normal distribution
normal distribution
Genotype
/
Phenotype correlation ![]() Heritability
Heritability
Genotypic expression depends on environment
Heritability
(h2) estimates proportion of phenotypic variation
due to genetic variation
Genotype / Environmental interaction
is variable (& unpredictable)
The Norm of
Reaction describes this
Heritability is not inevitability
Genetics is not destiny
Variation can be quantified (review)
mean ![]() standard deviation:
standard deviation: ![]()
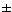
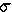
variance: ![]() 2
2
coefficient
of
variation (CV)
=
(![]() /
/![]() ) x 100
) x 100
CV removes effect of size when
comparing variance:
Ex.: Suppose
X = whale length Y =
tail width
X = 100 ![]() 1.0 versus Y = 1.0
1.0 versus Y = 1.0 ![]() 0.1
0.1
CV of X =
1% CV of Y
= 10%
Y is more variable, though ![]() X is larger
X is larger
Variation follows "normal distribution" (bell-curve)
iff
Multiple loci are
involved (quantitative)
Each
locus has about equal effect
(additive)
Each
locus acts independently
[interaction variance (see below) is minimal]
Ex.: Suppose a trait is influenced by 5
loci, each with two alleles A & a
A contributes 2
units to phenotype, a
contributes 1 unit
Range of contributions = (2u aa : 3u
Aa: 4u AA)5
mean = 30
units , range 20 ~ 40 units
(AaBbCcDdEe)
vs (aabbccddeeff ~ AABBCCDDEEFF)
35 = 243 genotype classes => variation continuous
Variation has two sources: genetic
(![]() 2G) & environmental (
2G) & environmental (![]() 2E) variance
2E) variance
phenotypic
variance ![]()
![]() 2P =
2P = ![]() 2G +
2G + ![]() 2E+
2E+ ![]() 2GxE
2GxE
additive
variance ![]()
![]() 2A =
2A = ![]() 2G +
2G + ![]() 2E
2E
heritability ![]() h2 =
h2 = 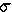 2G
/
2G
/
![]() 2A =
2A = ![]() 2G / (
2G / (![]() 2G +
2G + ![]() 2E)
2E)
"heritability in the narrow sense" ![]() additive variance
additive variance
heritability h2 is the fraction due to variance in genotypes
assumes
genotype / phenotype relationship is independent of environment
ignores ![]() 2GxE
2GxE ![]() interaction
variance:
interaction
variance:
genotype / phenotype relationship differs in different
environments.
Ex.: same strain of corn produces different
yields in different
conditions
Artificial breeding indicates that organismal
variation is highly heritable
Artificial selection
on agricultural species
Commercially
useful traits can be improved by selective
breeding
Common
Garden experiments
Correlation / Regression analysis
shows association between variables
For
many traits
in many organisms:
CV
= 5 ~ 10 %
h2
= 0.5 ~ 0.9
The Norm of
Reaction
mediates genotype through
environment to
produce phenotype
single-genotype
traits
two-genotype
traits
Genetics & Society
"Is it Genetic?"
Myth 1: That which is heritable is purely genetic
phenotypic
variance ![]()
![]() 2P
=
2P
= ![]() 2G
2G
[ignore ![]() 2E ,
2E , ![]() 2GxE]
2GxE]
Myth
2: That which is genetic is
fixed
& unchangeable
All text material © 2013 by Steven M. Carr