
What is
a "Gene" ?
A "gene"
occurs over a particular physical region (locus) of a double-stranded dsDNA molecule. It
includes an RNA-coding
region, where transcription occurs from the DNA template strand so as to synthesize
an RNA transcript in
the 5'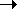 3' direction, running between the initiation
and termination sites.
3' direction, running between the initiation
and termination sites.
In scientific papers and databases, a gene sequence is
typically shown as that of the single-stranded sense (non-template,
partner) strand, in the 5'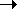 3' direction, between the first base
(+1)
corresponding to the
beginning of the start codon
and the last base corresponding to the end of the stop codon. Control
regions for transcription (promoters and terminators) occur immediately outside the
coding sequence. By convention, the gene is written "left to right" in the 5'
3' direction, between the first base
(+1)
corresponding to the
beginning of the start codon
and the last base corresponding to the end of the stop codon. Control
regions for transcription (promoters and terminators) occur immediately outside the
coding sequence. By convention, the gene is written "left to right" in the 5'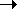 3'
direction of the sense strand: the
region to the 'left'
of the gene is called 'upstream'
and the region to the 'right'
is 'downstream'.
3'
direction of the sense strand: the
region to the 'left'
of the gene is called 'upstream'
and the region to the 'right'
is 'downstream'.
Note again that "left
/ right' and "top
/ bottom" are arbitrary, whereas 5'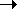 3' is a physical property of the
molecule. The coding region of eukaryotic genes typically
consists of a series of expressed exons with
intervening introns. Other
promoters and control elements may occur well outside the
region shown here, both upstream and downstream.
3' is a physical property of the
molecule. The coding region of eukaryotic genes typically
consists of a series of expressed exons with
intervening introns. Other
promoters and control elements may occur well outside the
region shown here, both upstream and downstream.