Traditional versus Phylogenetic classification of Vertebrata

Traditional versus Phylogenetic classification of Vertebrata
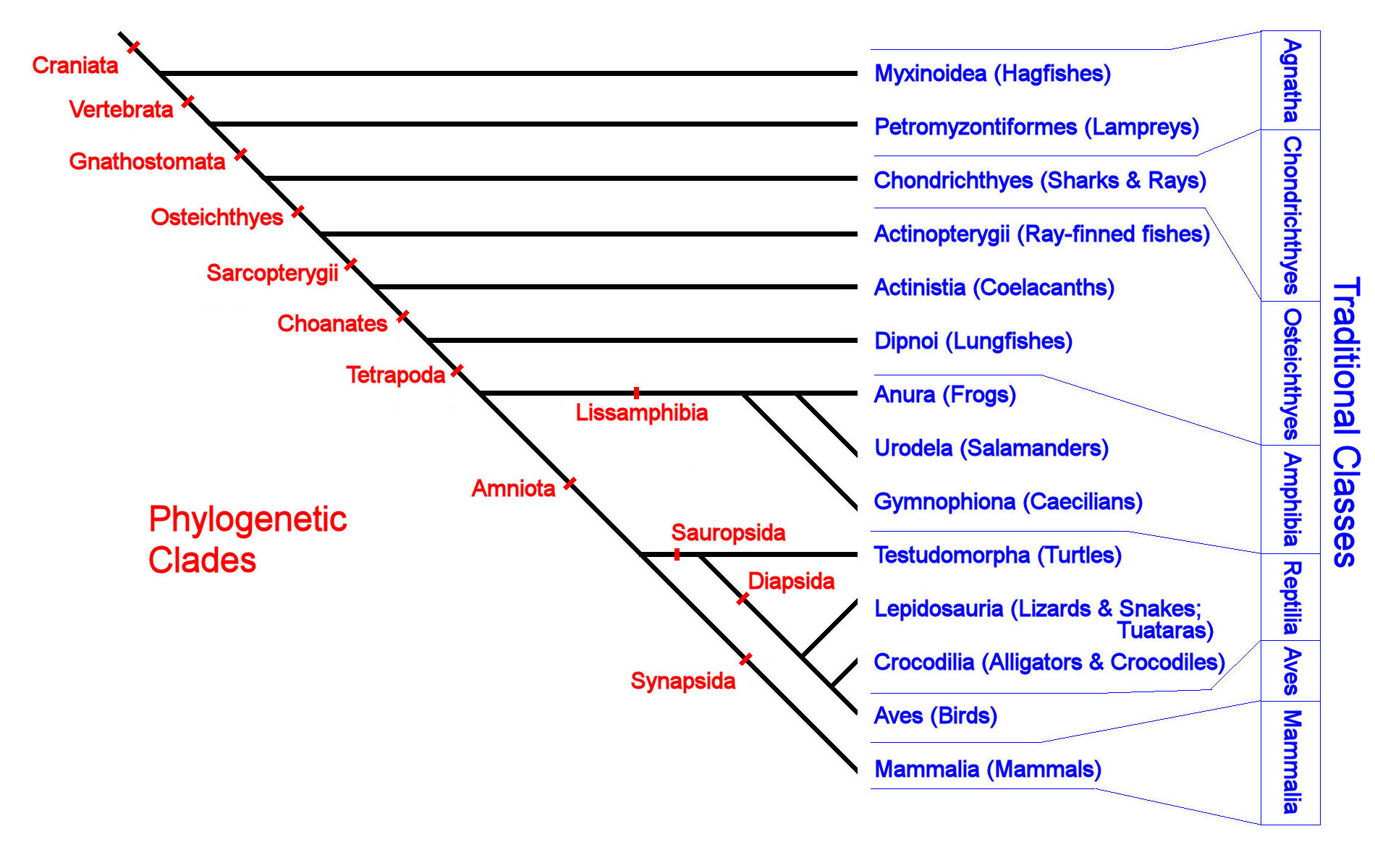
Vertebrates are those animals that have a backbone. The traditional system (right-hand column) recognizes seven taxonomic Classes of living Vertebrata: Agnatha [jawless "fish"], Chondrichthyes [cartilaginous "fish"], Osteicthyes [bony fish], Amphibia [scaleless tetrapods], Reptilia [scaly tetrapods], Aves [feathered bipeds], and Mammalia [hairy tetrapods]. Note that many of these classes are defined by "absence" characters ("jawless," "scaleless"). An eighth class of early fish-like creatures with a distinctive jaw articulation, Placodermi, is wholly extinct.
In the phylogenetic system (branching tree at left), taxonomic groups are defined by shared evolutionary characters (indicated by red crossbars) that defined a series of nested groups. For example, mammals (Mammalia) are an evolutionary lineage within Vertebrata [presence of backbone] that is defined successively as Gnathostomata [hinged, opposable jaws], Tetrapoda [four pentadactyl limbs], Amniota [amniotic egg membrane], and Synapsida [single temporal opening in the skull]. Note that the traditional recognition character "hair" for living mammals is not used, because hair first evolved in their early "reptilian" synapsid ancestors. "Reptiles" and "Aves" are both classified as Diapsida [two temporal openings in the skull], and "Fish" are separated into several groups, including the "fleshy-finned" Sarcoptyergia, which are more closely related to terrestrial tetrapods.
The phylogenetic
system accurately reflects the evolutionary history of
Vertebrates, but requires recognition of unfamiliar characters,
notably the number and position of openings in the skull. The
traditional system reflects certain impressions about shared
similarities among organisms that may be misleading. For
example, hagfish and lampreys resemble each
other in being "jawless"
[as are redwood trees], where the hagfish lineage separated
before the evolution of jaws, and the lamprey lineages
originally had jaws but lost them as an adaptation for their
parasitic lifestyle. They are otherwise quite distinct: for
example, hagfish do not have a true backbone, and the
braincase of lampreys resembles that of the gnathostomes. Early
tetrapods had scales: the three living orders of "scaleless"
amphibia probably lost scales independently as parallel
adaptation for dermal respiration. Thus it is not the case that
scaleless "amphibians" evolved into scaly "reptiles"