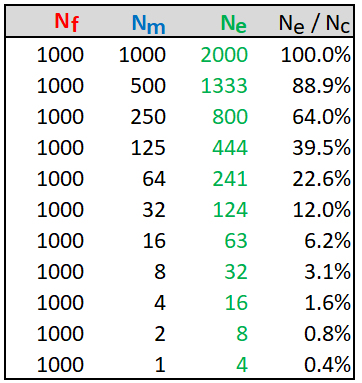
Ne with unequal sex ratios in a breeding population
In many species, a very small
number of individuals of one sex or the other do most or
almost all of the breeding. Recall that under these
conditions, Ne
= (4)(Nm)(Nf) / (Nm + Nf).
As the sex ratio increase, the effective population
number (Ne) falls rapidly as
a fraction of the population census count (Nc).
In the extreme case, where a single individual of either sex
is the only breeding individual, Ne
= 4, no matter how large the census count. A notable
example is Elephant Seals (Mirounga angustirostris),
where a single
alpha male has sole reproductive access to a
so-called 'harem' comprising 90% of more of the
breeding females. The reciprocal example is the hive of
eusocial insects, where a single female "queen"
has access to several hundred "drones" and is
the parent of 10s of 1,000s of workers, all of whom are
half-sisters.
HOMEWORK: In the table above, the total population size Nc drops as the number of males Nm decreases. Repeat the calculation, and adjust Nf so that total Nc = 2,000. Compare the numbers and graphs for the two calculations.
HOMEWORK: In the table above, the total population size Nc drops as the number of males Nm decreases. Repeat the calculation, and adjust Nf so that total Nc = 2,000. Compare the numbers and graphs for the two calculations.
Figure & Text material © 2021 by Steven M. Carr