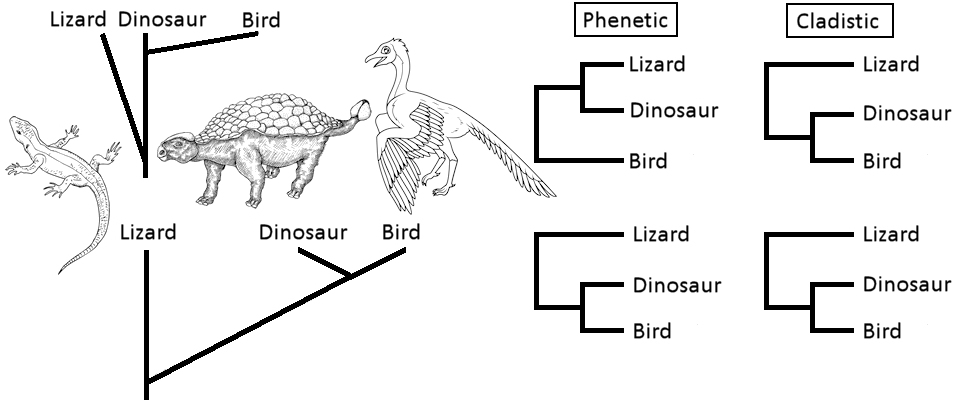
Phenetic versus Cladistic perceptions on the
classification of Birds

Phenetic versus Cladistic perceptions on the
classification of Birds
Given the phylogeny at top left, a traditional phenetic classification scheme (above, middle) emphasizes the perceived dissimilarity of birds from scaly tetrapods like lizards and crocodiles. A cladistic scheme (above, right) emphasizes the more recent common ancestry of birds with crocodiles.
Modern phylogenetic
classifications emphasize character analyses, which
show that birds evolved from dinosaurs. For example,
crocodiles, birds, and (presumably) dinosaurs have four-chambered
hearts and vocalizations, unlike lizards.That is,
perceptions of bird distinctiveness from dinosaurs have
changed. However, popular discussions, such as the "Jurassic
Park" franchise, present this change in perception
as showing that "dinosaurs are more similar to birds."
That is, perceptions of dinosaur "primitiveness" have changed. This "neo-phenetic"
analysis (left & middle, below) re-produces the phylogenetic
pattern from phenetic criteria. The cladistic
classification remains unchanged (below, right).
A note on
terminology: Systematists favoring a combination of
phenetic and cladistic approaches versus those who use
only cladistics, both claim to be doing phylogenetic
taxonomy. This term is now associated with cladistic
taxonomy, whereas phenetics remains associated with 'traditional'
taxonomy.