
Genetic
variation in
salinity tolerance of Mytilus edulis mussels
Leucine Amino Peptidase (LAP) is an enzyme
that cleaves peptide bonds adjacent to Leucine residues
in proteins. In the Blue
Mussel (Mytilus edulis), the
electrophoretic allele lap94
at the leucine amino peptidase (lap)
locus produces a form of the enzyme that has been
shown experimentally to function optimally in saline
environments. In Long Island Sound east of New York City,
there is a strong salinity gradient beginning with
freshwater in more westerly locations through increasingly
brackish sites eastward (sites 1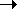 8), where salinity
reaches nearly the same level as that on the sea-ward side
of Long Island (sites 9
8), where salinity
reaches nearly the same level as that on the sea-ward side
of Long Island (sites 9 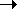 11). The frequency of the lap94 allele
increases in a cline (a
linear geographic trend) as a local adaptation to
local salinity and gene flow between adjacent
locations. Variation of LAP is a well-documented
case of biochemical adaptation, in which differences
among alleles at the same locus produce different genotypes,
that are expressed as different phenotypes variably adaptive
in different environments.
11). The frequency of the lap94 allele
increases in a cline (a
linear geographic trend) as a local adaptation to
local salinity and gene flow between adjacent
locations. Variation of LAP is a well-documented
case of biochemical adaptation, in which differences
among alleles at the same locus produce different genotypes,
that are expressed as different phenotypes variably adaptive
in different environments.
Homework: In no more than three sentences, describe the differences between the enzyme LAP, the gene locus lap, and the allele lap94 . Is the allele lap94 part of the genotype or of the phenotype? Explain.
Homework: I have used the word adaptation in two different senses. What are they? How are they similar? How are they different?
Homework: In no more than three sentences, describe the differences between the enzyme LAP, the gene locus lap, and the allele lap94 . Is the allele lap94 part of the genotype or of the phenotype? Explain.
Homework: I have used the word adaptation in two different senses. What are they? How are they similar? How are they different?