
Schematic Diagram of DNA structure, synthesis, & replication
Each DNA strand is a polynucleotide chain
with an alternating (S)ugar-(P)hosphate
backbone connected to one of four bases (A, C,
G, or T) .The two strands are anti-parallel,
as defined by their 5' 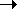 3'
orientation. The strands are joined by two or three
H-bonds, between A/T or C/G bases,
respectively.
3'
orientation. The strands are joined by two or three
H-bonds, between A/T or C/G bases,
respectively.
During duplication of the double-stranded molecule (replication), the old strands separate. New bases are added to either strand at the 3' end only, according to the base pairing rules: the 5' end remains unmodified. That is, the extension (synthesis) process on either strand occurs only in the 5'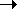 3'
direction. Replication of the
double-stranded molecule involves synthesis on single
strands, running in opposite directions with respect to
the 5'
3'
direction. Replication of the
double-stranded molecule involves synthesis on single
strands, running in opposite directions with respect to
the 5' 3'
orientation.
3'
orientation.
HOMEWORK: The diagram is schematic. Identify at lease one major feature of the process that is mis-represented.
During duplication of the double-stranded molecule (replication), the old strands separate. New bases are added to either strand at the 3' end only, according to the base pairing rules: the 5' end remains unmodified. That is, the extension (synthesis) process on either strand occurs only in the 5'
HOMEWORK: The diagram is schematic. Identify at lease one major feature of the process that is mis-represented.
Figure ©2004 Griffiths et al.; all text material ©2024 by Steven M. Carr