
Synthesis
of complementary DNA
(cDNA) from mRNA
by reverse transcription
mRNA (with a poly-A
tail) is isolated from an organism of interest. A short 5'-TTTT-3' DNA primer is
synthesized at the 3' end
of the message, and extended 5'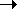 3' by the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which "reverses" the Central Dogma
by synthesizing a single-stranded
DNA molecule from the mRNA
template. The DNA strand
is thus complementary
to the mRNA. The 3' end of the ssDNA can fold back on itself
to form a single-stranded "hairpin loop", and
produce a short dsDNA region. The mRNA is removed by treatment
with NaOH. DNAPol I
is then added, which extends the double-stranded region as a primer
for synthesis of a new DNA strand.
The single-stranded portion of the loop is cut with a nuclease. The result is a double-stranded
cDNA that includes only the exon
portions of the gene, and not the introns,
which were spliced out of the hnRNA
template to make mRNA.
3' by the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which "reverses" the Central Dogma
by synthesizing a single-stranded
DNA molecule from the mRNA
template. The DNA strand
is thus complementary
to the mRNA. The 3' end of the ssDNA can fold back on itself
to form a single-stranded "hairpin loop", and
produce a short dsDNA region. The mRNA is removed by treatment
with NaOH. DNAPol I
is then added, which extends the double-stranded region as a primer
for synthesis of a new DNA strand.
The single-stranded portion of the loop is cut with a nuclease. The result is a double-stranded
cDNA that includes only the exon
portions of the gene, and not the introns,
which were spliced out of the hnRNA
template to make mRNA.
Figure © 2002 by Griffiths et al.; all text material © 2024 by Steven M.
Carr

