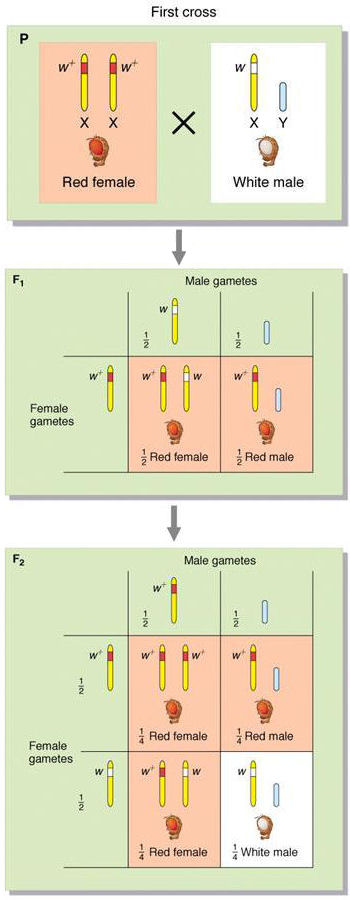
Sex-linked cross in Drosophila
A white-eyed mutant Drosophila appeared spontaneously in a culture of wild-type red-eyed flies. When crossed to a red-eyed female (P generation), the offspring generation (F1)
were all red-eyed, as expected if the red allele were dominant to the
white. When two F1 red-eyed flies were crossed, the offspring
generation (F2) showed a 3:1 ratio
of red-eyed to white-eyed flies, superficially as expected. However,
all of the white-eyed flies were male, so that one-half of all males
were white-eyed. The intrepretation as shown above is that the
eye-colour locus is carried on the X-chromosome, of which males have
only one.