
King & Wilson (1975) on the genetic similarity between Humans & Chimps
M-C King & AC Wilson (1975)
used Protein Electrophoresis to compare genetic
variation at n = 88 alleles from 42 loci
between Humans (Homo sapiens) and Chimps (Pan
troglodytes). Their Table 2 data are
summarized here. For each allele, si
is the product of the frequencies of each allele in the two
species, and for each locus, Si
is the sum of si for its
alleles. Thus, for the three alleles at locus AP, Si
= (0.29)(0.0) + (0.68)(1.00) + (0.03)(0.0) =
0.68. Si estimates the similarity
at each locus between species, that is, the
probability that a pair of alleles drawn at random, one
from each species, will be identical.
A majority of loci are either fixed (n = 17) for alternative alleles, or identical (n = 13) for the same allele, in the two species. This simplifies calculation of the average genetic similarity (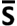 ) across
loci, because Si = 1 or 0,
respectively, for each locus in these two classes. For
variable loci, the contribution is the product of the number
of loci and the average value across loci. Then,
) across
loci, because Si = 1 or 0,
respectively, for each locus in these two classes. For
variable loci, the contribution is the product of the number
of loci and the average value across loci. Then, 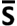 = [(17 x
0) + (13 x 1) + (12 x 0.708)] / 42 = 0.512.
= [(17 x
0) + (13 x 1) + (12 x 0.708)] / 42 = 0.512.
If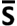 estimates Similarity, then D = (1 -
estimates Similarity, then D = (1 - 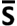 )
estimates Distance, which in the case would be
simply D = (1 - 0.512) = 0.488. The accuracy
of this estimate can be improved by applying the Poisson
Correction for multiple hits. For these
electrophoretic data, the correction is D' = -ln(
)
estimates Distance, which in the case would be
simply D = (1 - 0.512) = 0.488. The accuracy
of this estimate can be improved by applying the Poisson
Correction for multiple hits. For these
electrophoretic data, the correction is D' = -ln(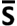 )
= 0.670, a correct of 31% = 0.670 / 0.512.
)
= 0.670, a correct of 31% = 0.670 / 0.512.
A majority of loci are either fixed (n = 17) for alternative alleles, or identical (n = 13) for the same allele, in the two species. This simplifies calculation of the average genetic similarity (
If
Data arrangement & Text material © 2025 by Steven M. Carr