
Mutagenicity across the electromagnetic spectrum
Planck's equation [ E = h / 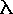 , where E = energy,
, where E = energy, 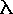 = wavelength, h =
Planck's constant ] predicts an inverse relationships
between radiation wavelength and energy. At the
left-hand end of the spectrum, long-wave
radiation in
general has low energy
and is not mutagenic. High-energy microwaves can cook biological
organisms, but not mutagenize them. At the right-hand end of the
spectrum, short-wave
radiation such at UV,
X- & Gamma rays has high energy, and are
progressively more mutagenic.
For example, tanning beds use predominantly long-wave UV A (400 ~ 315
nm) radiation just beyond the visible range, which is less
mutagenic than short-wave UV
B (315 ~ 280 nm) radiation further to the right.
= wavelength, h =
Planck's constant ] predicts an inverse relationships
between radiation wavelength and energy. At the
left-hand end of the spectrum, long-wave
radiation in
general has low energy
and is not mutagenic. High-energy microwaves can cook biological
organisms, but not mutagenize them. At the right-hand end of the
spectrum, short-wave
radiation such at UV,
X- & Gamma rays has high energy, and are
progressively more mutagenic.
For example, tanning beds use predominantly long-wave UV A (400 ~ 315
nm) radiation just beyond the visible range, which is less
mutagenic than short-wave UV
B (315 ~ 280 nm) radiation further to the right.
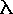 , where E = energy,
, where E = energy, 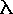 = wavelength, h =
Planck's constant ] predicts an inverse relationships
between radiation wavelength and energy. At the
left-hand end of the spectrum, long-wave
radiation in
general has low energy
and is not mutagenic. High-energy microwaves can cook biological
organisms, but not mutagenize them. At the right-hand end of the
spectrum, short-wave
radiation such at UV,
X- & Gamma rays has high energy, and are
progressively more mutagenic.
For example, tanning beds use predominantly long-wave UV A (400 ~ 315
nm) radiation just beyond the visible range, which is less
mutagenic than short-wave UV
B (315 ~ 280 nm) radiation further to the right.
= wavelength, h =
Planck's constant ] predicts an inverse relationships
between radiation wavelength and energy. At the
left-hand end of the spectrum, long-wave
radiation in
general has low energy
and is not mutagenic. High-energy microwaves can cook biological
organisms, but not mutagenize them. At the right-hand end of the
spectrum, short-wave
radiation such at UV,
X- & Gamma rays has high energy, and are
progressively more mutagenic.
For example, tanning beds use predominantly long-wave UV A (400 ~ 315
nm) radiation just beyond the visible range, which is less
mutagenic than short-wave UV
B (315 ~ 280 nm) radiation further to the right.Figure 1997 by Klug & Cummings; All text material (c) 2024 by Steven M. Carr