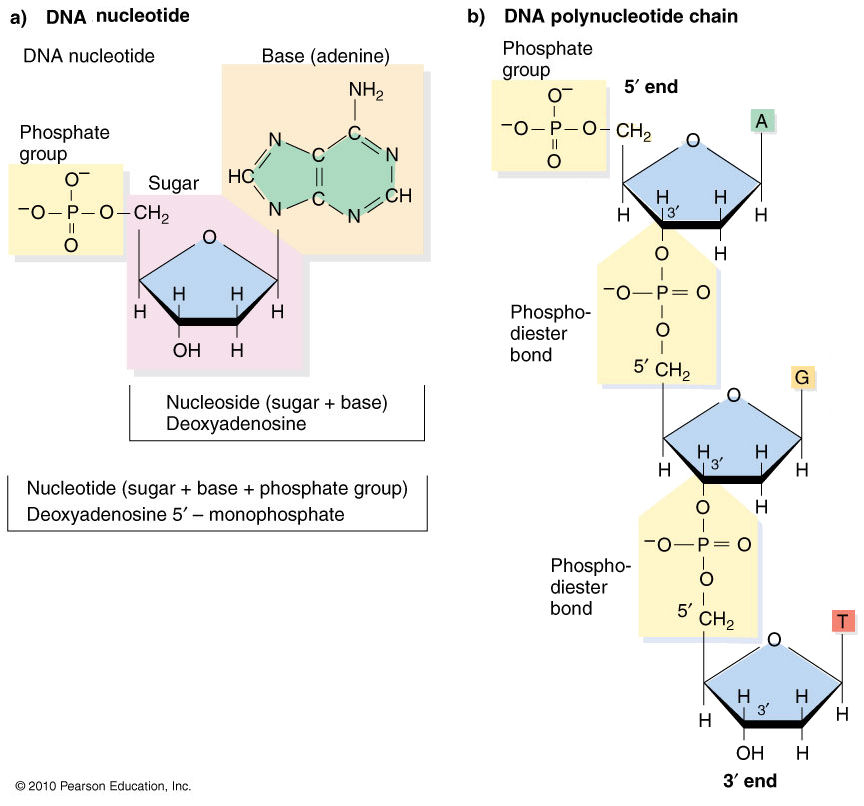
Structure of a nucleoside triphosphate (= nucleotide) & Polynucleotide
In
Figure (a), the base is attached to the 1'-C
of sugar, and the inorganic phosphate to
the 5'-C. The pentose (5-carbon) sugar is
identifiable as a deoxyribose by the absence
of an -O- from the hydroxyl group on the 2'-C.
In Figure (b), the first nucleotide is oriented 5' 3'.
Successive nucleotides are added at the 3' end, such
that the 5' end always remains unchanged,
and the 3' end "changes" as it "grows."
This pattern is referred to as 5'
3'.
Successive nucleotides are added at the 3' end, such
that the 5' end always remains unchanged,
and the 3' end "changes" as it "grows."
This pattern is referred to as 5' 3'
elongation. All DNA biochemical transaction
take place 5'
3'
elongation. All DNA biochemical transaction
take place 5' 3': do not
think about or try to describe them in any other
way.
3': do not
think about or try to describe them in any other
way.
In Figure (b), the first nucleotide is oriented 5'
Figure © 2012 TA Brown, Introduction to Genetics (1st
ed.); additional text © 2024 by Steven M. Carr