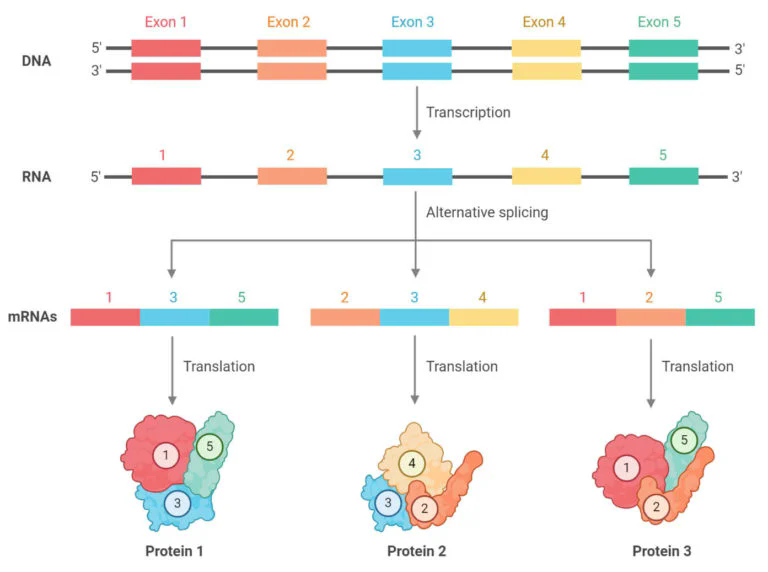
Alternative exon combinations can lead to different proteins
The
primary hnRNA transcript includes both exon-
& intron-equivalent sequences. The exon-equivalents
(numbered) may correspond to functional domains of the
protein, for example, DNA-binding regions or
enzymatic activities. By removing one or more exon-equivalent
regions along with the intron-equivalents, different
proteins with different functions can be produced.
Alternative splicing may explain why genomes can get along with far fewer protein-coding regions than expected.
Alternative splicing may explain why genomes can get along with far fewer protein-coding regions than expected.
Text © 2024 by Steven M. Carr