
T1 Bacteriophages ("Phages")


T1 Bacteriophages ("Phages")
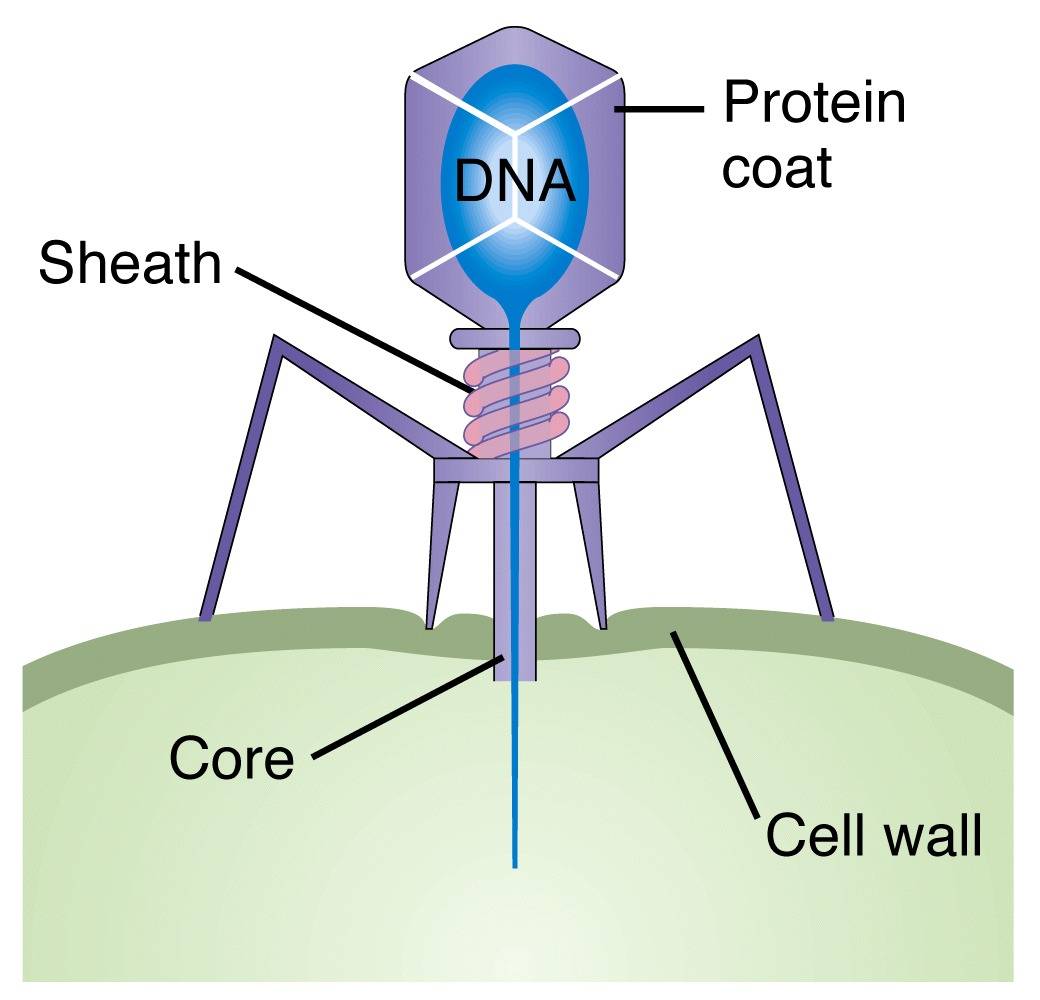
Bacteriophages are viruses that attack bacteria. The name means "bacteria eaters" and is commonly shortened to just "phage". Phage particles comprises a "head" that contains DNA packaged within a protein coat, and a hollow "tail" by which they attach to the outside membrane of bacteria. The phage DNA is injected into the bacterium, where it uses the cell's replication machinery to reproduce itself. Production of new phage particles causes the host cell to rupture ("lyse") and release the phage, which go on to infect other bacteria. Early biochemical and genetic studies of phage are the foundations of modern molecular biology.