The
Cytoskeleton of the cell

Made up
of intermediate filaments, microfilaments and microtubules.
Each have
their own architecture of protein and protein subunits, and form higher
networks through irreversible cross links of individual rods.
Functions
include, but
are not limited to:
-
control
of
location of mitotic cleavage plane
-
maintenance
of cell shape
-
transport
of
molecules and organelles in cells
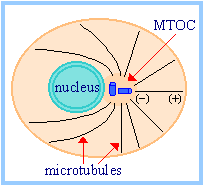

Cytoskeletal
rods form
linear polymers and have polarity
In
microtubles and
microfilaments the end of the rod at the centre of the cell is deemed “-“ and is located at the microtubule organizing
centre
(MTOC). The peripheral ends of each rod are deemed the “+” end.
ATP is
hydrolyzed for
energy to propel movement along a microtubule.


Kinesin is a protein that
moves from the “-“ to the “+” of a
microtubule and
carry vesicles to the periphery of the cell. The motor is contained it
the
globular head which interacts with the microtubule, and the molecule is
attached by the tail.